Sedation Monitoring and Safety Protocols
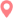
Sedation Monitoring and Safety Protocols are crucial elements in ensuring the well-being of pediatric patients during dental procedures. It is essential for the sedation dentist to closely monitor vital signs throughout the sedation process to promptly address any potential complications that may arise. In Barstow, California, Sedation Dentists are trained to maintain a high level of vigilance and adhere to strict safety protocols to guarantee the safe administration of sedation to children.
Continuous monitoring of vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation levels, allows the sedation dentist to assess the patient’s response to sedation and make necessary adjustments to ensure their comfort and safety. Additionally, the presence of emergency equipment and medications is essential to address any unforeseen adverse reactions promptly. Sedation Dentists in Barstow, California, undergo specialized training to implement these monitoring and safety protocols effectively, minimizing risks and maximizing the positive outcomes of sedation dentistry for pediatric patients.
Vital Sign Monitoring
Vital sign monitoring is a crucial aspect of sedation dentistry, especially when administering sedation to pediatric patients. Sedation Dentists in Commerce, California have a responsibility to closely observe the child’s vital signs throughout the sedation process to ensure their safety and well-being. This includes monitoring parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation levels, and respiratory rate to detect any abnormalities or signs of distress promptly.
Continuous vital sign monitoring allows the Sedation Dentist in Commerce, California to promptly address any changes in the child’s condition and take appropriate action if necessary. By closely monitoring these vital signs, the dentist can ensure the child’s comfort and safety while undergoing dental procedures under sedation. Therefore, meticulous attention to vital signs is a fundamental safety measure in pediatric sedation dentistry, providing reassurance to both the dental team and the child’s caregivers.
PostSedation Care and Recovery Process
After the sedation procedure, children will require close monitoring during the recovery process. Observation of vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation is crucial to ensure that the child is recovering safely. Sedation Dentist in Corona Del Mar, California will closely monitor the patient’s condition to watch for any signs of complications or adverse reactions.
Following the sedation, it is important for children to adhere to activity restrictions to prevent any potential risks. Sedation Dentist in Corona Del Mar, California will provide specific instructions on what the child can eat or drink post-sedation, as well as advise on limitations regarding physical activities. It is essential for parents or guardians to closely follow these guidelines to ensure the child’s well-being during the recovery period.
Activity Restrictions
Activity restrictions following sedation for children are crucial to ensure their safety and well-being. After receiving sedation from a Sedation Dentist in Calabasas, California, children must avoid engaging in any strenuous physical activities or operating heavy machinery for a designated period of time. These restrictions are essential to prevent any potential accidents due to drowsiness or impaired motor skills that may result from the sedative medications.
Additionally, it is recommended that children do not consume heavy meals immediately after sedation to prevent any nausea or vomiting. Sedation Dentists in Calabasas, California emphasize the importance of providing a calm and quiet environment for children post-procedure to facilitate their recovery process. By adhering to these activity restrictions and promoting a relaxing atmosphere, parents and caregivers can ensure that children have a smooth and safe recovery after sedation.
Importance of Pediatric Dentists in Sedation Dentistry
For parents seeking dental care involving sedation for their children, the expertise of a pediatric dentist is paramount. A Sedation Dentist in Barstow, California with specialized training in pediatric sedation dentistry is equipped to cater to the unique needs of young patients. These professionals possess the skills and knowledge required to administer sedation in a safe and effective manner, ensuring the comfort and well-being of children undergoing dental procedures.
Pediatric dentists play a crucial role in sedation dentistry by not only administering the appropriate type and dosage of sedation but also by closely monitoring the child throughout the procedure. Their understanding of child psychology and behavior enables them to create a calming environment that helps alleviate anxiety and fear in young patients. By choosing a Pediatric Sedation Dentist in Barstow, California, parents can rest assured that their child’s dental experience will be handled with the utmost care and expertise.
Specialized Training Requirements
To become a sedation dentist in Claremont, California, specialized training requirements must be met to ensure the safe and effective administration of sedation to pediatric patients. Pediatric dentists who provide sedation services undergo extensive training beyond their general dental education. This training includes specific coursework on sedation techniques, knowledge of different types of sedatives, and understanding the pediatric population’s unique needs when it comes to sedation.
Moreover, sedation dentists in Claremont, California, must also undergo rigorous clinical training to practice administering sedation in a controlled environment. This hands-on experience allows them to develop the skills necessary to monitor vital signs, adjust medication dosages as needed, and handle any complications that may arise during the sedation process. By meeting these specialized training requirements, sedation dentists can ensure the highest level of care and safety for their pediatric patients.
FAQS
What types of sedation are commonly used for children during dental procedures?
The most common types of sedation used for children during dental procedures include nitrous oxide (laughing gas), oral sedatives, and intravenous (IV) sedation.
Is it safe to sedate children during dental procedures?
When administered by trained professionals following strict safety protocols, sedating children during dental procedures is generally considered safe and effective.
How are vital signs monitored during sedation for children?
Vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels are closely monitored throughout the sedation process to ensure the child’s safety and well-being.
What are some common activity restrictions after sedation for children?
After sedation, children may be advised to avoid strenuous physical activities, operate heavy machinery, or make important decisions for a specified period to allow the sedative effects to wear off completely.
Why is it important to have pediatric dentists for sedation dentistry?
Pediatric dentists are specially trained to provide dental care to children, including administering sedation in a safe and effective manner tailored to the unique needs of pediatric patients.
What specialized training do pediatric dentists undergo for sedation dentistry?
Pediatric dentists undergo additional training in sedation techniques, pediatric anesthesia, and managing emergencies to ensure the highest level of safety and care when sedating children during dental procedures.”””
Related Links
Sedation Dentist
Do dentists still sedate?
Can you choose to be sedated at the dentist?
Why is sedation not covered by dental insurance?
Who is a candidate for sedation dentistry?
What is considered minimal sedation?
What is the minimum age for inhalation sedation?
What is considered moderate sedation in dentistry?
Who is qualified to administer moderate sedation?
What is the scale for moderate sedation?
What are the 5 levels of sedation?
Who is authorized to administer conscious sedation to a patient?
Is oral sedation considered general anesthesia?